APPLICATIONS
3D Slicer
3D Slicer is a free, open source and multi-platform software package widely used for medical, biomedical, and related imaging research ([Fedorov_2012]).
Official resources
Configure 3D Slicer on the HIP in order to use modules and extensions
Important
These configuration steps only need to be performed once.
This section explains how to configure 3D Slicer so extra modules and extensions from the “Extensions Manager” can be installed.
Start 3D Slicer in a new Desktop and take the following steps:
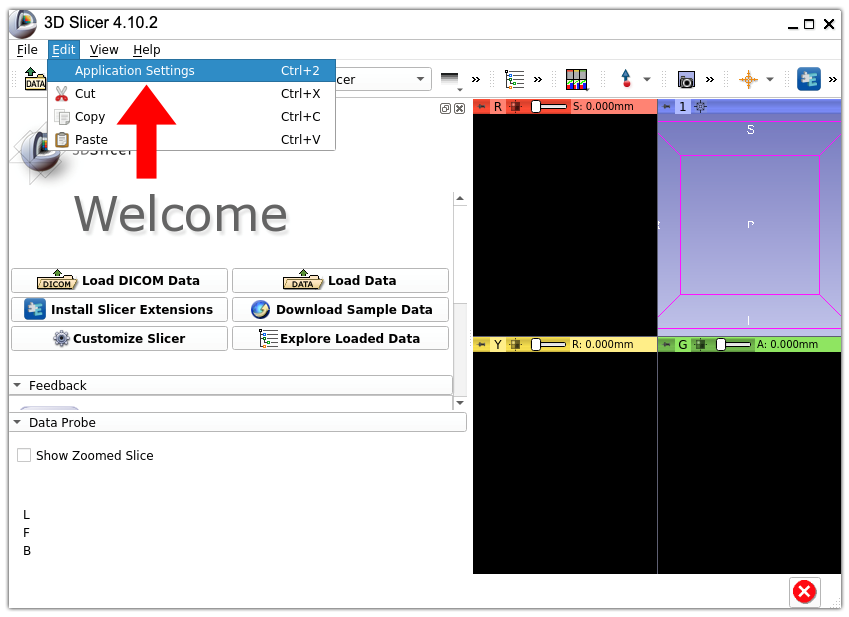
1. Open 3D Slicer settings. In the menu bar, select “Edit” > “Application Settings”.
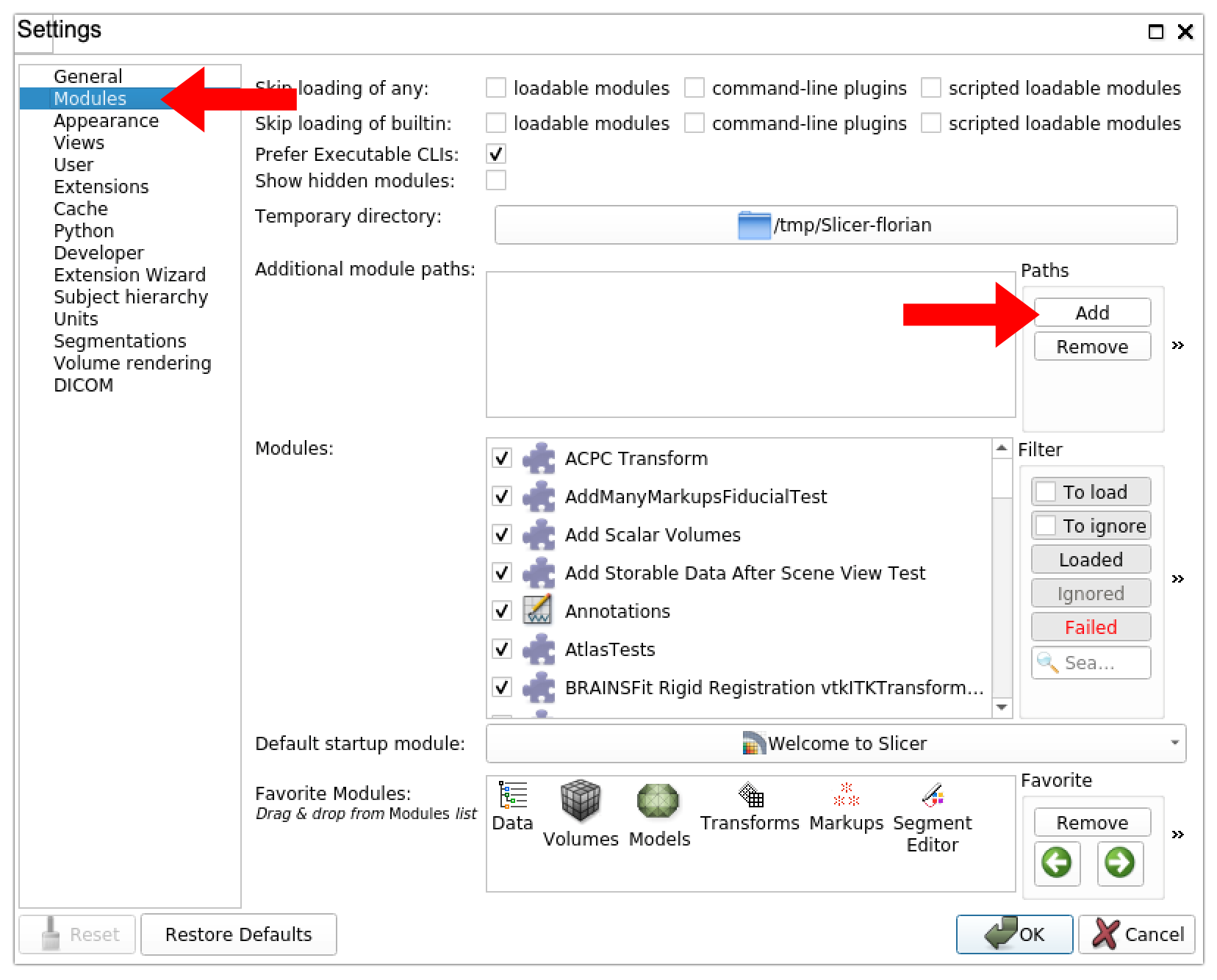
2. Add a new module path. In the “Settings” side menu, select “Modules” and click on the “Add” button under the “Paths” section. This will open a file browser.
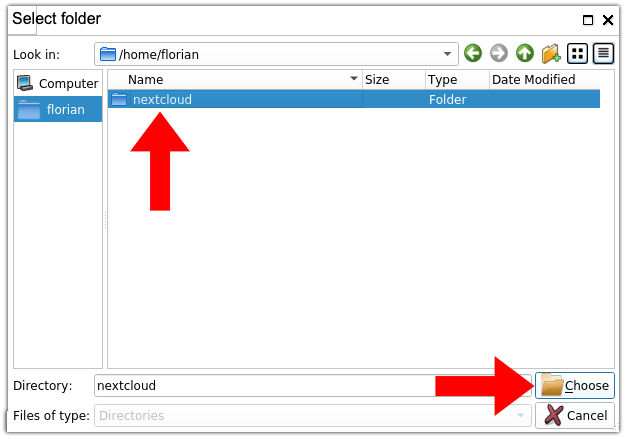
3. Select your nextcloud folder. In the file browser, browse to your /home/<HIP_USER> directory where <HIP_USER> is your HIP username and select the “nextcloud” folder before clicking on the “Choose” button. The file browser will close itself.
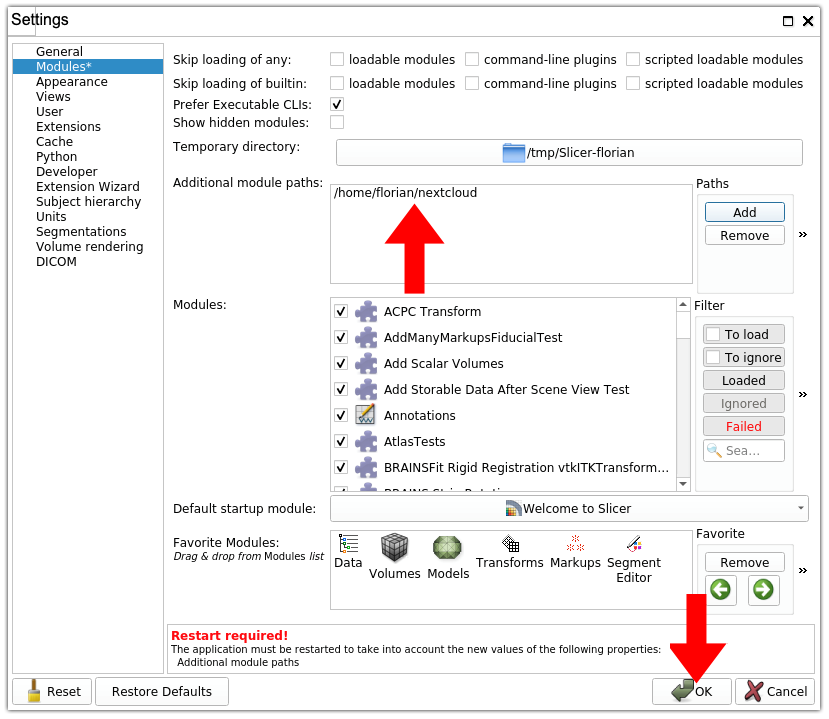
4. Save modifications. The path to your nextcloud folder should now appear in the panel titled “Additional module paths”. At the bottom of the “Settings” window, click on the “OK” button to save your modifications.
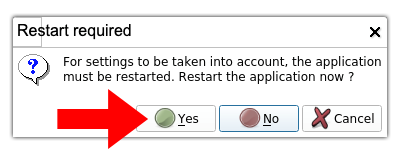
5. Restart 3D Slicer. A pop-up window will ask you to restart 3D Slicer. Click “Yes”.
3D Slicer will automatically close itself but will not restart. Please wait for the application to be fully shutdown and restart it manually.
You are now ready to install and use extensions from 3D Slicer “Extensions Manager”:
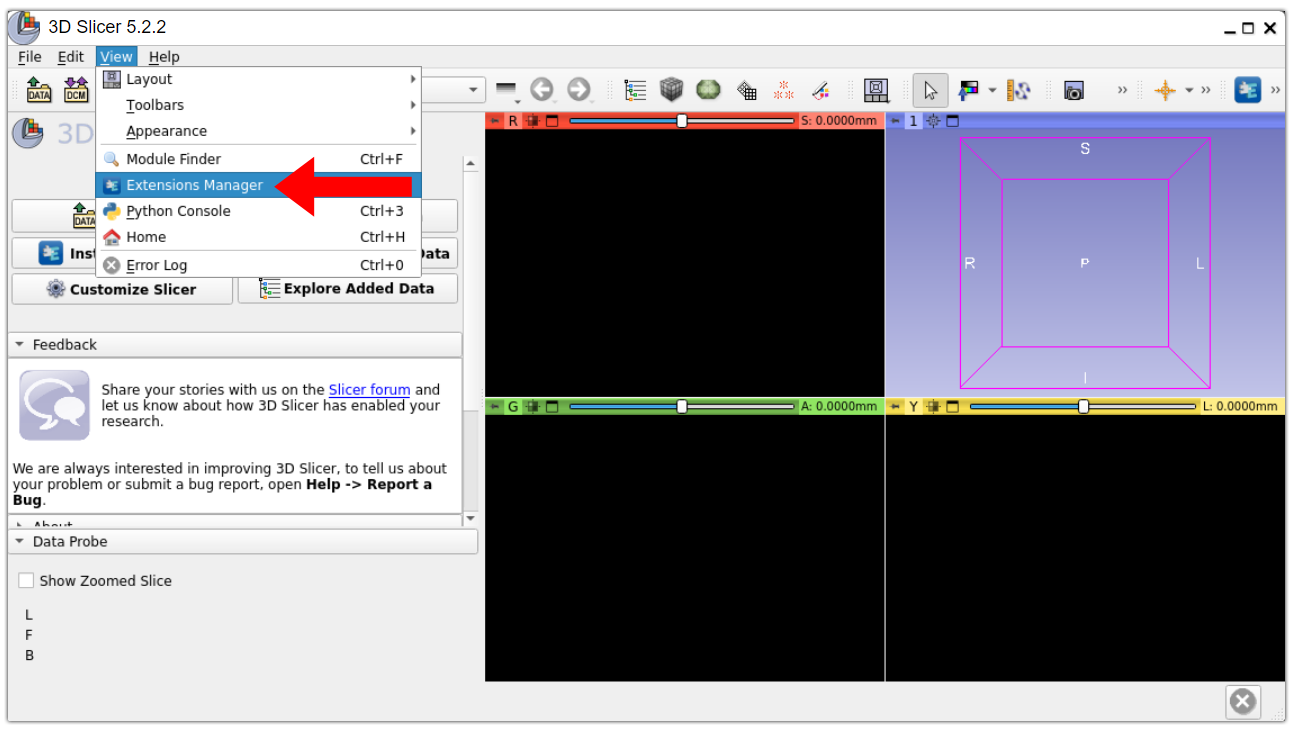
6. Open 3D Slicer Extensions Manager. In the menu bar, select “View” > “Extensions Manager”.
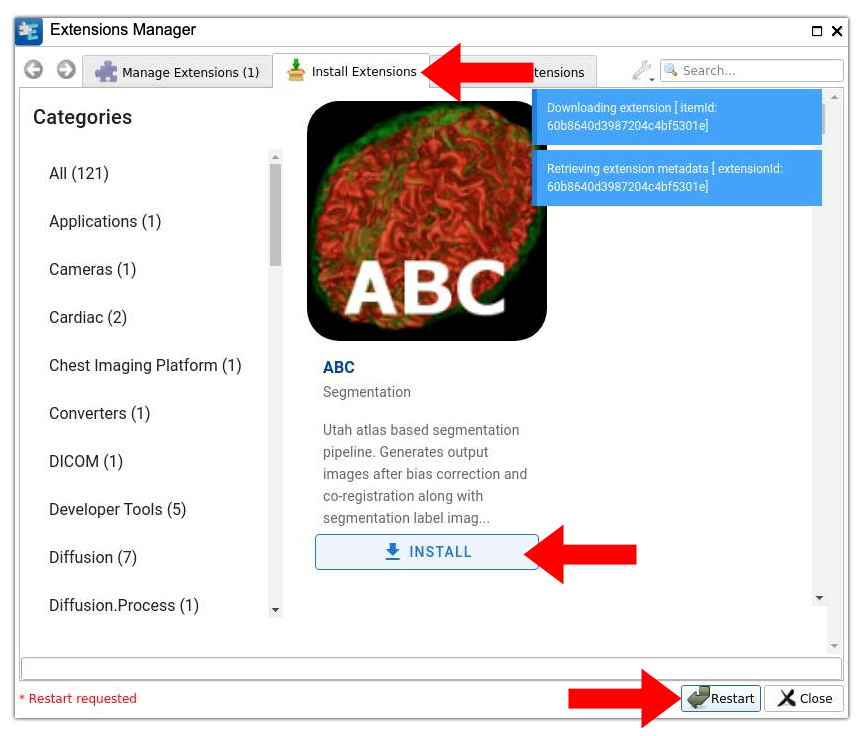
7. Install extensions. The middle tab “Install Extensions” lets you browse and install new extensions from an online catalog. Seamlessly install the desired extensions by clicking on the associated “INSTALL” button. You will have to restart 3D Slicer after installing new extensions as prompted in the interface. Remember that 3D Slicer will automatically close itself but needs to be restarted manually. The left tab “Manage Extensions (X)” where X is the number of installed extensions, lets you disable and/or uninstall any previously installed extensions.
References
Fedorov A, Beichel R, Kalpathy-Cramer J, Finet J, Fillion-Robin J-C, Pujol S, Bauer C, Jennings D, Fennessy FM, Sonka M, Buatti J, Aylward SR, Miller JV, Pieper S, Kikinis R. 3D Slicer as an Image Computing Platform for the Quantitative Imaging Network. Magnetic Resonance Imaging., 2012, 30(9):1323-41.
AnyWave
AnyWave is a software designed to easily open and view data recorded by EEG or MEG acquisition systems. AnyWave is modular and can load additionnal plug-ins to enhance its features and capabilities ([Colombet_2015]).
Official resources
References
Colombet B, Woodman M, Badier JM, Bénar CG. AnyWave: a cross-platform and modular software for visualizing and processing electrophysiological signals. Journal of neuroscience methods 242., 2015, 118-26.
BIDS Manager
BIDS Manager is a Python package to collect, organise and manage neuroscience data in Brain Imaging Data Structure (BIDS) format ([Roehri_2021]). Find more information regarding the BIDS standard on the official website and the associated documentation.
Official resources
References
Roehri N, Medina Villalon S, Jegou A, Colombet B, Giusiano B, Ponz A, Bartolomeo F, Bénar CG. Transfer, Collection and Organisation of Electrophysiological and Imaging Data for Multicentre Studies. Neuroinform., 2021.
Brainstorm
Brainstorm is an application dedicated to the analysis of brain recordings: MEG, EEG, fNIRS, ECoG, depth electrodes and multiunit electrophysiology ([Tadel_2011]).
Official resources
HIP resources
The following HIP tutorials are available:
References
Tadel F, Baillet S, Mosher JC, Pantazis D, Leahy RM. Brainstorm: A User-Friendly Application for MEG/EEG Analysis. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience., 2011.
dcm2niix
dcm2niix is designed to convert neuroimaging data from the DICOM format (standard image format generated by modern medical imaging devices) to the NIfTI format ([Li_2016]).
Official resources
References
Li X, Morgan PS, Ashburner J, Smith J, Rorden C. The first step for neuroimaging data analysis: DICOM to NIfTI conversion. J Neurosci Methods., 2016, 264:47-56.
FileManager (PCManFM)
FileManager (PCManFM) is a Qt-based file manager which uses GLib for file management. FileManager (PCManFM) helps you organize, list, and locate files and directories on the HIP.
Official resources
License
FileManager (PCManFM) is licensed under the terms of the GPLv2 or any later version.
Freesurfer
Freesurfer is a an open source neuroimaging toolkit for processing, analyzing, and visualizing human brain MR images. Freesurfer is developed by the Laboratory for Computational Neuroimaging at the Athinoula A. Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging.
Official resources
References
If you use Freesurfer in your research, use the dedicated page to cite the relevant publication(s).
Frites
Frites is a Python toolbox for assessing information-theorical measures on human and animal neurophysiological data (M/EEG, Intracranial). The aim of Frites is to extract task-related cognitive brain networks (i.e modulated by the task). The toolbox also includes directed and undirected connectivity metrics such as group-level statistics ([Combrisson_2022a], [Combrisson_2022b]).
Official resources
References
Combrisson E, Allegra M, Basanisi R, Ince RAA, Giordano BL, Bastin J, Brovelli A. Group-level inference of information-based measures for the analyses of cognitive brain networks from neurophysiological data. Neuroimage. 2022 Sep;258:119347. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2022.119347. Epub 2022 May 31. PMID: 35660460.
Etienne Combrisson, Ruggero Basanisi, Vinicius Lima Cordeiro, Robin A. A Ince and Andrea Brovelli. (2022). Frites: A Python package for functional connectivity analysis and group-level statistics of neurophysiological data. Journal of Open Source Software, 7(79), 3842, https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.03842
FSL
FSL is a comprehensive library of analysis tools for FMRI, MRI and DTI brain imaging data ([Jenkinson_2012]).
Official resources
References
Jenkinson M, Beckmann CF, Behrens TE, Woolrich MW, Smith SM. FSL. NeuroImage., 2012, 62:782-90.
GARDEL
GARDEL is a tool for automatic segmentation and labelization of SEEG contacts ([Medina_2018]).
Official resources
References
Medina Villalon S, Paz R, Roehri N, Lagarde S, Pizzo F, Colombet B, Bartolomei F, Carron R, Bénar CG. EpiTools, A software suite for presurgical brain mapping in epilepsy: Intracerebral EEG. J Neurosci Methods. 2018 Jun 1;303:7-15. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2018.03.018. Epub 2018 Mar 29. PMID: 29605667.
HiBoP
HiBoP is an application dedicated to the visualization of intracranial brain recordings such as intracranial electroencephalography (iEEG), cortico-cortical evoked potentials (CCEP) and functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI).
Official resources
Documentation and executables (Linux, MacOS, Windows) are available in the GitHub repository.
Acknowledgements
This open source software code was developed in part or in whole in the Human Brain Project, funded from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 Framework Programme for Research and Innovation under the Specific Grant Agreement No. 785907 (Human Brain Project SGA2).
Warning
This application is not yet available on the HIP.
IntrAnat
IntrAnat is a free database and visualization software for Intracranial Electroencephalographic (iEEG) data that allows to locate and register intracerebral electrodes for individual cases as well as for group studies ([Deman_2018a]).
Official resources
References
Deman P, Bhattacharjee M, Tadel F, Job AS, Rivière D, Cointepas Y, Kahane P, David O. IntrAnat Electrodes: A Free Database and Visualization Software for Intracranial Electroencephalographic Data Processed for Case and Group Studies. Front Neuroinform., 2018, 12:40.
LibreOffice
LibreOffice is a free and open-source office productivity software suite. The LibreOffice suite consists of programs for word processing, creating and editing of spreadsheets, slideshows, diagrams and drawings, working with databases, and composing mathematical formulae. LibreOffice uses the OpenDocument standard as its native file format, but supports formats of most other major office suites, including Microsoft Office, through a variety of import and export filters.
Official resources
Localizer
Localizer is an application whose goal is to take raw brain recordings and process them to obtain the frequency responses using a combination of band pass filter and Hilbert Envelope.
Official resources
Warning
This application is not yet available on the HIP.
MATLAB
MATLAB is a proprietary multi-paradigm programming language and numeric computing environment developed by MathWorks ([MATLAB_2023]). MATLAB allows matrix manipulations, plotting of functions and data, implementation of algorithms, creation of user interfaces, and interfacing with programs written in other languages.
Official resources
References
The MathWorks Inc. (2023). MATLAB version: 23.2 (R2023a), Natick, Massachusetts: The MathWorks Inc. https://www.mathworks.com
MNE-Python
MNE-Python is an open-source Python package for exploring, visualizing, and analyzing human neurophysiological data: MEG, EEG, sEEG, ECoG, NIRS ([Gramfort_2013]).
Official resources
References
Alexandre Gramfort, Martin Luessi, Eric Larson, Denis A. Engemann, Daniel Strohmeier, Christian Brodbeck, Roman Goj, Mainak Jas, Teon Brooks, Lauri Parkkonen, and Matti S. Hämäläinen. MEG and EEG data analysis with MNE-Python. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 7(267):1–13, 2013. doi:10.3389/fnins.2013.00267.
MRI Deface
MRI Deface is an automated Defacing Tools ([Bischoff-Grethe_2007]).
Official resources
References
Bischoff-Grethe A, Ozyurt IB, Busa E, Quinn BT, Fennema-Notestine C, Clark CP, Morris S, Bondi MW, Jernigan TL, Dale AM, Brown GG, Fischl B. A technique for the deidentification of structural brain MR images. Hum Brain Mapp. 2007 Sep;28(9):892-903. doi: 10.1002/hbm.20312. PMID: 17295313; PMCID: PMC2408762.
MRIcroGL
MRIcroGL is a cross-platform tool for viewing DICOM and NIfTI format images. It provides a drag-and-drop user interface as well as a scripting language. ([Rorden_2000]).
Official resources
References
Rorden C, Brett M. Stereotaxic display of brain lesions. Behav Neurol., 2000, 12(4):191-200.
Mrtrix3
MRtrix3 provides a set of tools to perform various types of diffusion MRI analyses, from various forms of tractography through to next-generation group-level analyses ([Tournier_2019]).
Official resources
References
Tournier, J-Donald, et al. “MRtrix3: A fast, flexible and open software framework for medical image processing and visualisation.” Neuroimage 202 (2019): 116137.
NiftyReg
NiftyReg is an open-source software for efficient medical image registration ([Modat_2010], [Modat_2014]). It contains routines to perform rigid, affine and non-linear registration of 2D and 3D images stored as Nifti or Analyze (nii or hdr/img).
Official resources
References
Modat, et al. (2010). Fast free-form deformation using graphics processing units. Computer Methods And Programs In Biomedicine,98(3), 278–284.doi:10.1016/j.cmpb.2009.09.002
Modat, et al. (2014). Global image registration using a symmetric block-matching approach. Journal of Medical Imaging, 1(2), 024003–024003.doi:10.1117/1.JMI.1.2.024003
RStudio
RStudio is an integrated development environment for R, a programming language for statistical computing and graphics ([RStudio_2020]).
Official resources
References
RStudio Team (2020). RStudio: Integrated Development for R. RStudio, PBC, Boston, MA URL http://www.rstudio.com/.
Warning
This application is not yet available on the HIP.
TRCAnonymizer
TRCAnonymizer is a software that, as his name suggests, allows you to check if your Micromed data file are anonymized and if not gives you the mean through a simple interface to do so.
Official resources
The Virtual Brain
The Virtual Brain (TVB) offers software for constructing, simulating and analysing brain network models including the TVB simulator; magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) processing pipelines to extract structural and functional brain networks; combined simulation of large-scale brain networks with small-scale spiking networks; automatic conversion of user-specified model equations into fast simulation code; simulation-ready brain models of patients and healthy volunteers; Bayesian parameter optimization in epilepsy patient models; data and software for mouse brain simulation; and extensive educational material ([Sanz_Leon_2013], [Schirner_2022]).
Official resources
HIP resources
The following HIP tutorials are available:
The Virtual Brain on the HIP
The Virtual Brain app on the HIP relies on Jupyter notebooks. Starting the app will actually starts JupyterLab Desktop, a cross-platform desktop application for JupyterLab. For additional information regarding Jupyter notebooks, please consult the official documentation.
References
Sanz Leon P, Knock SA, Woodman MM, Domide L, Mersmann J, McIntosh AR, Jirsa V. The Virtual Brain: a simulator of primate brain network dynamics. Front Neuroinform., 2013, 7:10.
Schirner M, Domide L, Perdikis D, Triebkorn P, Stefanovski L, Pai R, Prodan P, Valean B, Palmer J, Langford C, Blickensdörfer A, van der Vlag M, Diaz-Pier S, Peyser A, Klijn W, Pleiter D, Nahm A, Schmid O, Woodman M, Zehl L, Fousek J, Petkoski S, Kusch L, Hashemi M, Marinazzo D, Mangin JF, Flöel A, Akintoye S, Stahl BC, Cepic M, Johnson E, Deco G, McIntosh AR, Hilgetag CC, Morgan M, Schuller B, Upton A, McMurtrie C, Dickscheid T, Bjaalie JG, Amunts K, Mersmann J, Jirsa V, Ritter P. Brain simulation as a cloud service: The Virtual Brain on EBRAINS. Neuroimage., 2022, 251:118973.
VS code
Visual Studio Code, also commonly referred to as VS Code, is a source-code editor made by Microsoft with the Electron Framework, for Windows, Linux and macOS. Features include support for debugging, syntax highlighting, intelligent code completion, snippets, code refactoring, and embedded Git. Users can change the theme, keyboard shortcuts, preferences, and install extensions that add functionality.